Genome
A genome is an organism’s complete set of genetic material. Genomics is the study of genomes. In humans, a copy of the genome is found in nearly every cell in the body.
What does a genome do?
The genome contains both genes that provide the instructions for producing proteins (about 2% of the genome) and sequences that do not directly code for proteins (about 98% of the genome), often termed ‘non-coding’.
The function of the 98% of the genome that does not code directly for proteins is not fully understood, but parts are involved in gene regulation and others are important for maintaining the structure of the genome. Analysing these regions can be just as important as analysing genes when applying genomics in clinical practice.
How long is a genome?
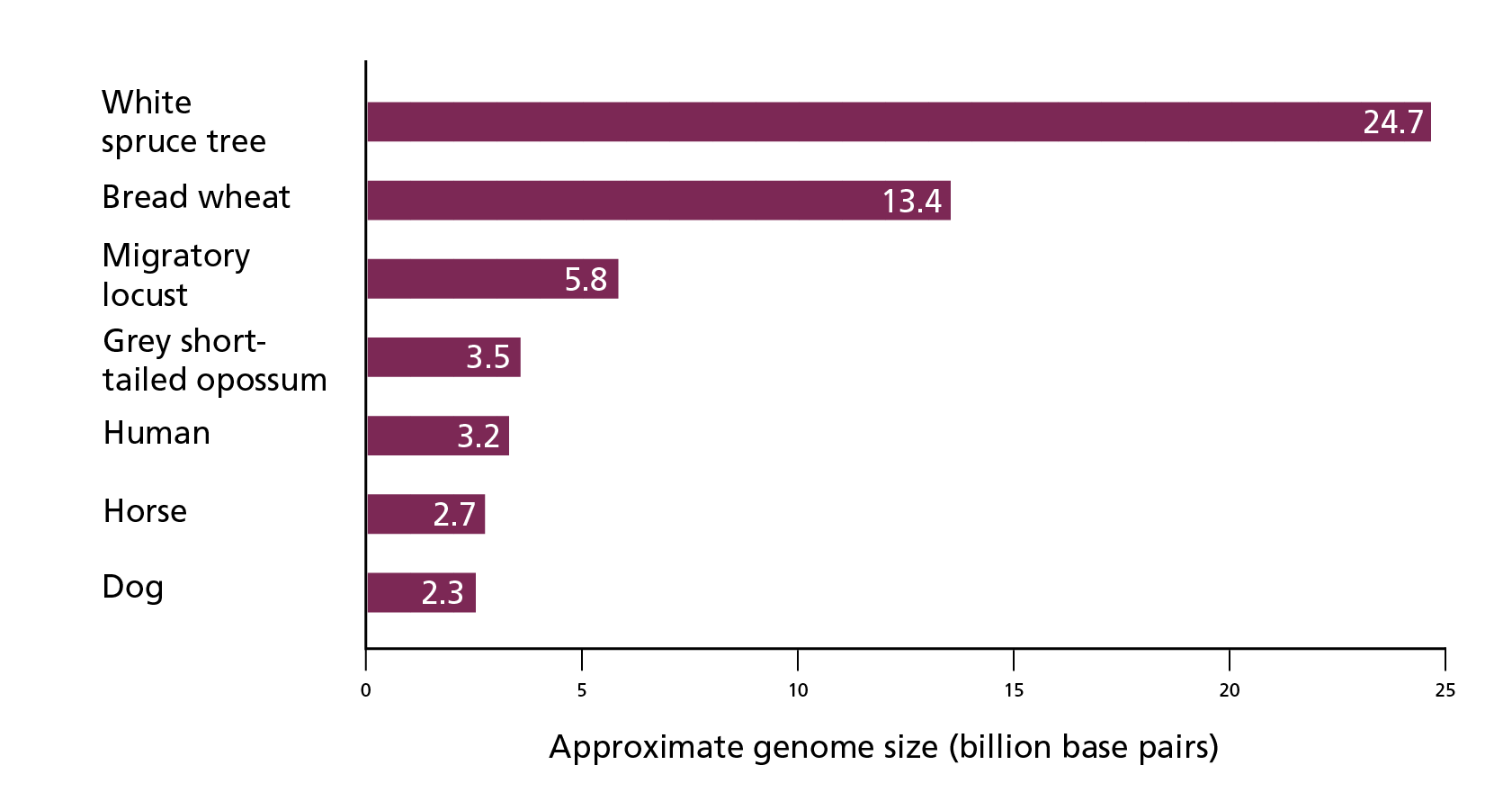
The length of the genome varies between species and doesn’t necessarily reflect the size of the organism from which it came (see figure 1). The human genome is approximately 3 billion base pairs (3.2 to be exact) in length.
Figure 1: Approximate genome size in different organisms
Where is the genome found?
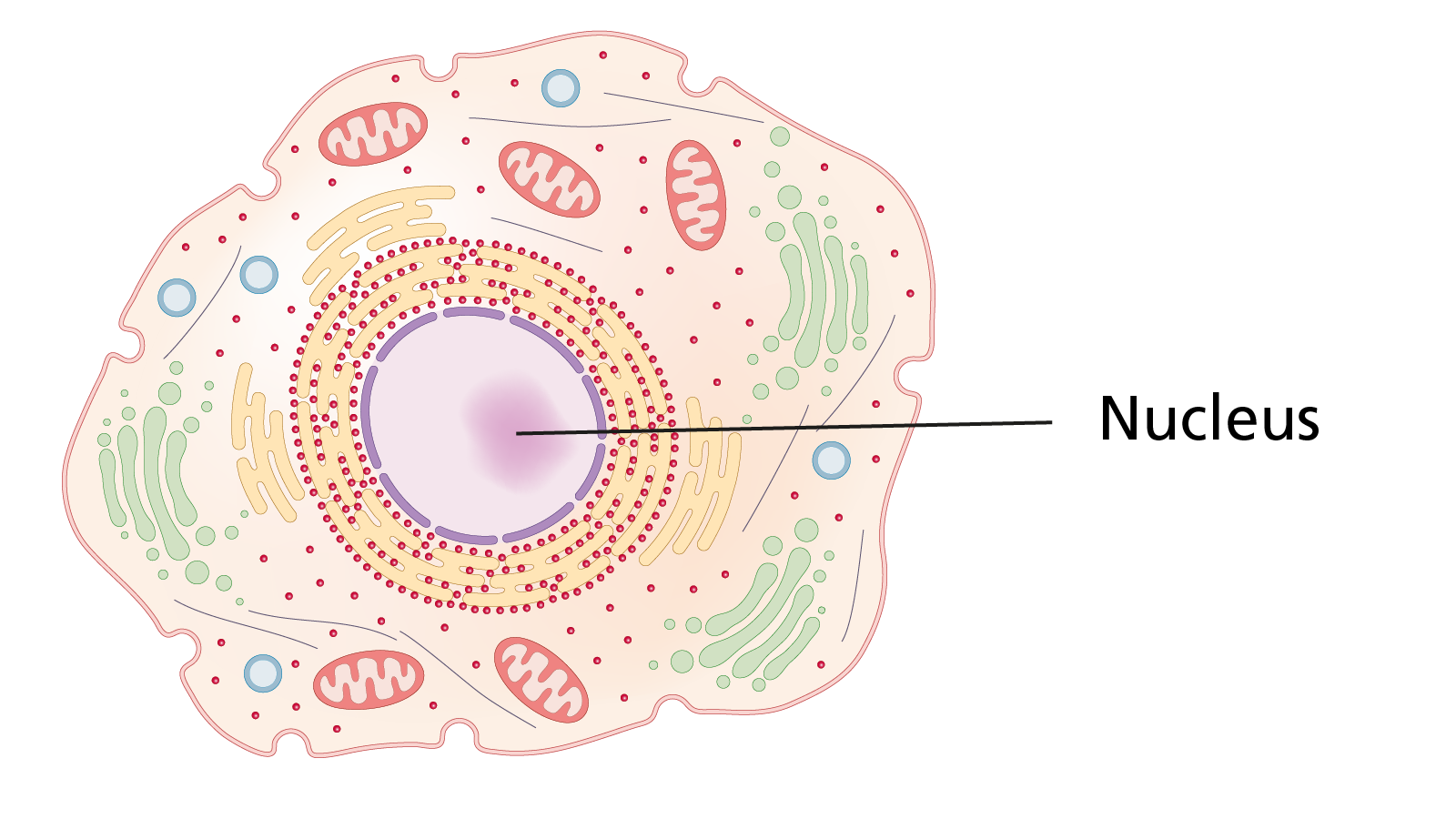
In organisms known as eukaryotes (which includes humans, other mammals, plants and fungi), most of the genome is found in the nucleus of the cell (see figure 2).
Figure 2: Cell nucleus where most of the eukaryotic genome is found
In humans and other complex multicellular organisms, a copy of the genome is found in nearly every cell in the body. The exception to this is mammalian red blood cells, which do not contain a genome as they do not have a nucleus or mitochondria.
Furthermore, human reproductive cells (eggs and sperm) each contain half the DNA from that person’s genome, which then combines to form a whole genome at fertilisation.
How is the genome organised?
Chromosomes
Most of the DNA in the cell’s nucleus is organised into structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is a double helix of DNA, coiled and folded into an efficient structure to fit into the nucleus.
Without this system of packaging, the DNA would not fit inside the cell. All the DNA from a single human cell stretched out would reach approximately six feet (180cm) in length.
In most cells there are two copies of each chromosome. The number of chromosomes that a species has varies, and does not necessarily reflect the size of the genome. For instance, the horse genome is organised into 32 pairs of chromosomes and is 2.7 billion bases long, whereas the human genome is organised into 23 pairs of chromosomes and is 3.2 billion bases long.
Figure 3: A cell with nucleus at its centre containing chromosomes
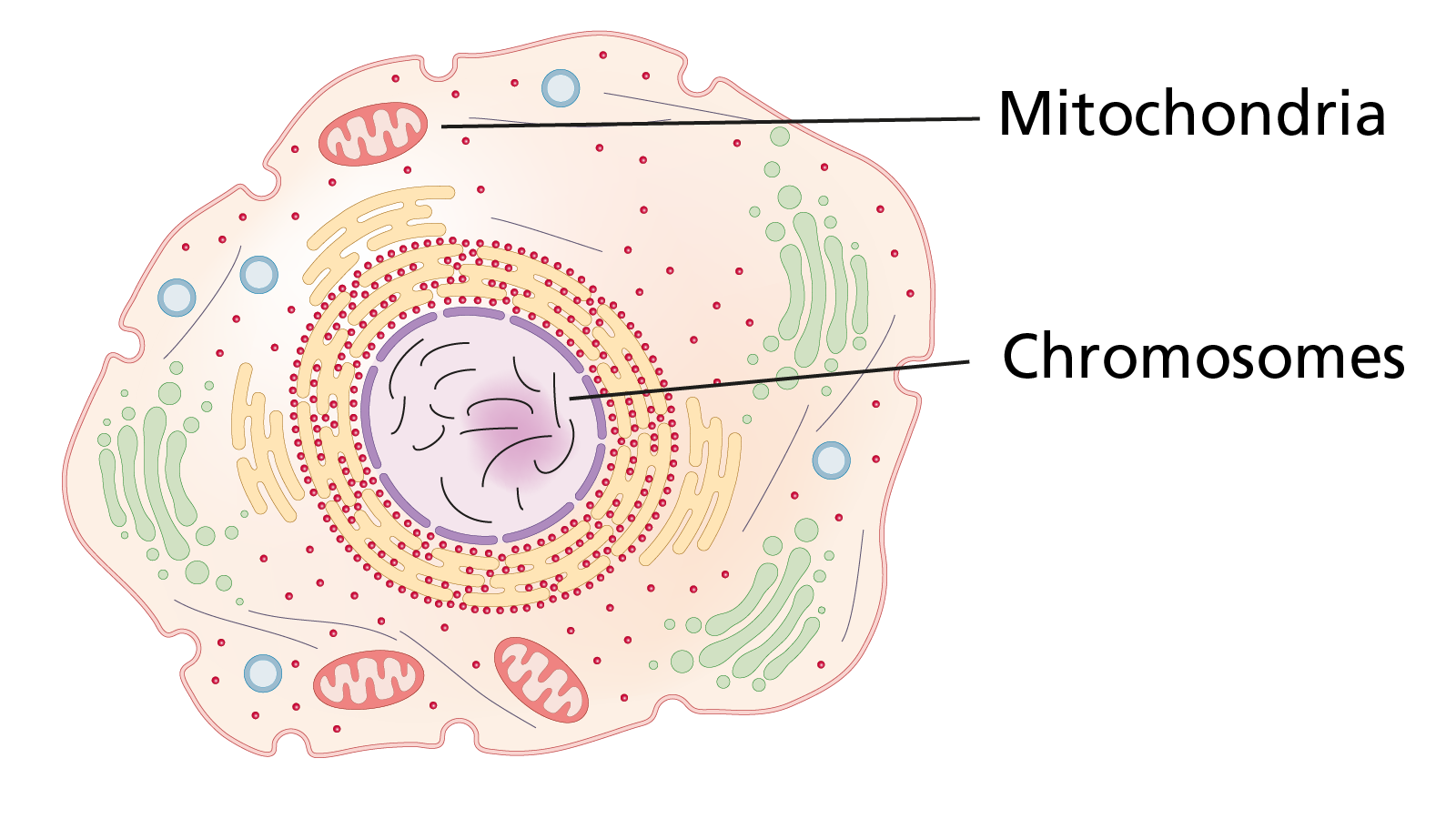
Human chromosomes
A human cell will usually contain 23 pairs of chromosomes. Twenty-two of these chromosomes are called autosomes. They are numbered from 1 through to 22. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are our sex chromosomes. Females have two X chromosomes, and males have an X and a Y chromosome.
Figure 4: Schematic of human chromosomes showing them lined up in pairs size order, with the sex chromosome pair last

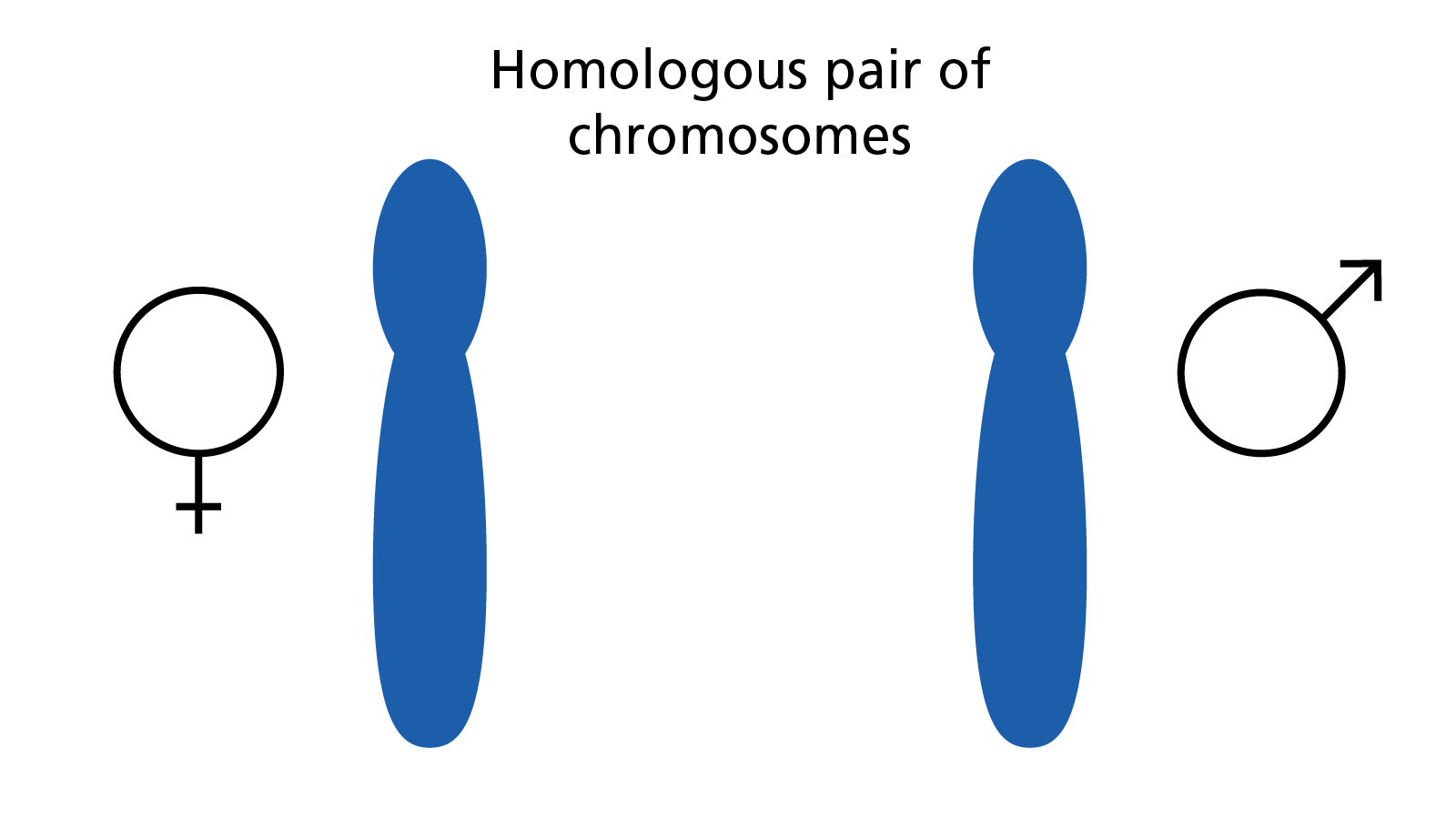
Homologues
The two chromosomes that make up each pair of autosomes are called homologues. Although homologues look similar, they are not exactly the same. In humans one chromosome of each homologous pair is inherited from the father, the other from the mother. As females have two X sex chromosomes, these too can be classed as homologues.
Figure 5: A pair of homologous chromosomes, one came from the individual’s mother, the other from their father
DNA outside the nucleus
Cells also contain structures called mitochondria (see figure 3), which are rather like the cell’s batteries, vital for turning energy from food into a form that can be used by cells. There are many thousands of mitochondria within each cell, especially in muscle and the brain.
These structures also contain a small amount of DNA, which forms less than 0.0005% of the total genome, about 16 thousand base pairs. Although it is only a small part of the genome, it is essential: without a functional mitochondrial genome, the cell will die.
Mitochondrial DNA is present as a complete circle, and it does not consist of homologous pairs like nuclear DNA. Unlike nuclear DNA, which is inherited from both the mother and the father, mitochondrial DNA is only inherited from the mother.
Key messages
- Every living organism has a genome.
- In humans a copy of the genome is found in nearly every cell.
- The human genome is organised into structures called chromosomes. In each cell humans have 46 chromosomes arranged into 23 pairs.
Resources
For clinicians
- NHS England Genomics Education Programme: Genomics 101: From Genes to Genome course